Macylab ICP-6800,the measurement of nine heavy metals in water
1、 Relevant standard requirements
The problem of heavy metal pollution in water is becoming more and more serious. Scientific and accurate analysis of heavy metals in water has become an essential task of environmental monitoring. The test results show that the detection limit, precision, accuracy and recovery rate of nine elements of cobalt, nickel, cadmium, barium, chromium, copper, lithium, manganese and strontium meet the requirements of the technical guidelines. It is proved that the analytical conditions of the laboratory meet the experimental requirements and have the ability to analyze nine elements.
With the aggravation of surface water pollution and people's increasing requirements for water ecological environment function, it is urgent to do a good job in water quality monitoring and analysis. Compared with other pollutants, heavy metal pollution in water pollution has long-term accumulation, which can cause physiological lesions and teratogenicity in organisms, and can enter the river bottom sediment and soil system, leading to secondary pollution of environmental factors. It is of great significance to monitor and analyze heavy metals in water for water quality supervision and governance. Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (icp-6800) has the advantages of simultaneous determination of multiple elements and simple and rapid analysis method compared with atomic absorption spectrophotometry. The purpose of this paper is to discuss the analysis and test of common heavy metals in water by ICP-OES with reference to《hj776-2015 determination of 32 elements in water quality by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry》.

2、Instrument and parameter setting
2.1 Instrument
ICP-6800 inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer(Macylab)
Atomization gas flow:0.70L/min;
Plasma cooling gas flow rate:1.0L/min;
Auxiliary gas flow:0.20L/min;
RF power:1300W;
Sample lifting time:30s,vertical observation.
2.2 reagents
24 element standard solution:the concentration is100μg/ml,Macylab(China) Co.,Ltd;
Nitric acid:high grade pure;
The purity of argon and nitrogen is more than or equal to 99.999%;
The resistance of ultrapure water is more than 18.2 m Ω.
2.3 establishment of standard curve
Due to the different response values of the instrument to different elements, curve 1 was prepared to determine cobalt, nickel, cadmium and barium respectively. 5.00 ml mixed element standard solution with concentration of 100 μ g / ml was accurately transferred into a 50 ml volumetric flask, and the standard reserve concentration of 10 μ g / ml was obtained by constant volume with (1 + 99) nitric acid solution to the scale. Add 0.00 ml, 1.00 ml, 2.00 ml, 4.00 ml and 7.00 ml standard solution into six 100 ml volumetric flasks, and fix the volume to the scale with (1 + 99) nitric acid solution to prepare standard solutions with concentration of 0.00 mg / L, 0.10 mg / L, 0.20 mg / L, 0.40 mg / L and 0.70 mg / L.
3、 Experimental process
Pretreatment for determination of soluble metal elements in clean surface water and groundwater: after water sample collection, filter through 0.45 μ M filter membrane, discard the initial 50-100ml solution, collect the required volume of filtrate, adjust the solution to pH < 2 with (1 + 1) nitric acid, and test on the computer.
4、 Results and errors
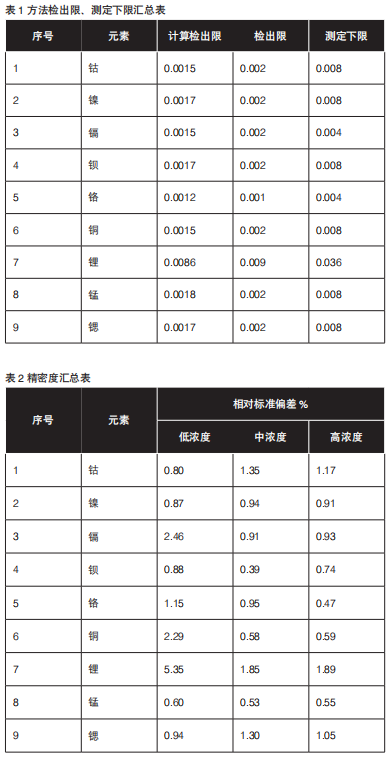
4.1 detection limit
According to hj168-2010 technical guidelines for the formulation and revision of environmental monitoring and analysis methods, if the target substance is not detected in the reagent blank, the sample with concentration or content 3-5 times of the detection limit of the estimated method shall be determined for 7 times in parallel, the standard deviation shall be calculated, and then the detection limit of the method shall be calculated according to the formula.
4.2 S-standard deviation
The following 9 elements are determined by the concentration of 3-5 times of the detection limit of the method, and the detection limits of the following elements are obtained. See the table below for details. The detection limits of cobalt, nickel, cadmium, barium, chromium, copper, lithium, manganese and strontium are 0.001 ~ 0.009mg/l, and the lower limits of determination are 0.004 ~ 0.036mg/l, which are far lower than the detection limits of the method.
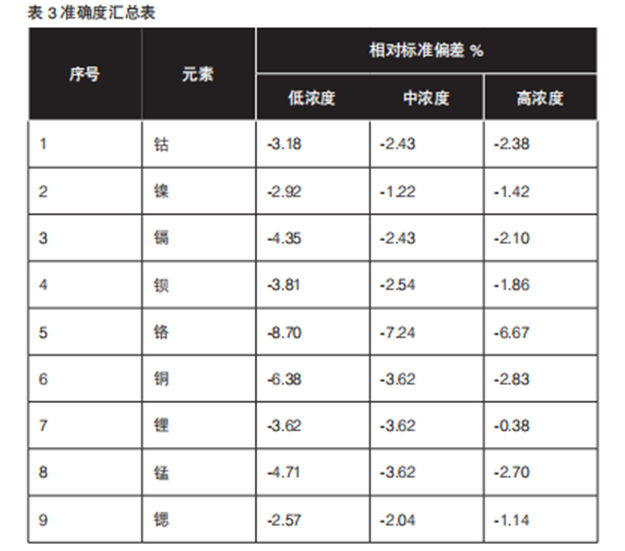
4.3 Precision
Precision is the degree of agreement between the measured values of a homogeneous sample repeatedly analyzed under controlled conditions using a specific analytical procedure. It reflects the size of random error existing in analysis method or measurement system. The smaller the random error is, the higher the precision is. The results are shown in Table 2. The relative standard deviation ranges from 0.39% to 5.35%. Except for the poor stability of element lithium at low concentration, the relative standard deviations of other elements are relatively low, which indicates that the error of reagent test and analysis process is small, the analysis process of the instrument is stable and the repeatability is good, and the precision test of the measured elements meets the requirements.
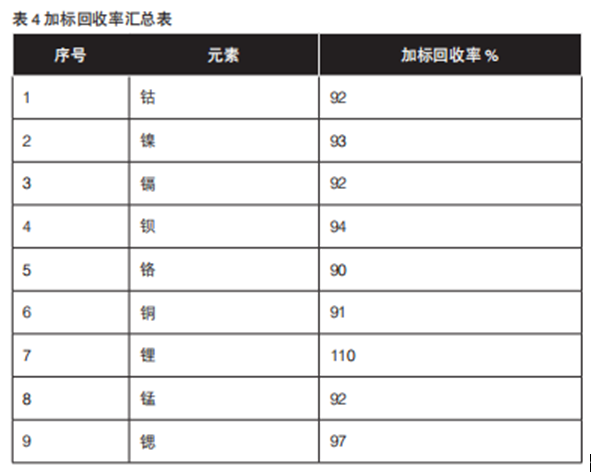
4.4 Accuracy summary
Accuracy is often used to measure the degree of agreement between the analysis results (the mean value of single measurement or repeated measurement) obtained by a specific analysis program and the assumed or recognized true value. The accuracy of an analysis method or analysis system is the comprehensive index of systematic error and random error existing in the method or measurement system, which determines the reliability of the analysis results. This paper tests the accuracy of cobalt, nickel, cadmium, barium, chromium, copper, lithium, manganese and strontium with three concentration solutions. The results are shown in Table 3. The relative deviation ranges from - 8.70% to - 0.38%. In the range of quality control values, there are many elements with low accuracy, and the accuracy of chromium is relatively low, which is preliminarily estimated to be caused by large interference.
4.5 Summary of spiked recoveries
Standard addition recovery is another indicator of test accuracy. A certain amount of standard sample was added into the actual sample to calculate the recovery. The recoveries of cobalt, nickel, cadmium, barium, chromium, copper, lithium, manganese and strontium ranged from 90% to 110%, as shown in Table 4. It shows that the random error and systematic error are small, and the whole analysis process is stable and reliable.
5、conclusion
The detection limits of cobalt, nickel, cadmium, barium, chromium, copper, lithium, manganese and strontium were 0.001 ~ 0.009mg/l and the lower limit of determination was 0.004 ~ 0.036mg/l, which were far lower than the detection limits of the method. The relative standard deviations of the nine elements were in the range of 0.39% ~ 5.35%. The results showed that the surface relative deviation was - 8.70% ~ 0.38%, and the recovery was 90% ~ 110%. The analytical method and reagents used meet the analytical requirements, and have the ability to analyze cobalt, nickel, cadmium, barium, chromium, copper, lithium, manganese and strontium in surface water and groundwater by using hj776-2015 determination of 32 elements in water quality by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry.




